Database Service: PostgreSQL with Docker¶
Overview
MedSync's data infrastructure is based on PostgreSQL, a powerful open-source object-relational database system.
By leveraging Docker, we can effortlessly initiate the PostgreSQL service, automatically setting up the initial database, roles, and passwords using environment variables.
Why SQLAlchemy and Alembic?¶
-
SQLAlchemy: This is an ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) library for Python. It allows you to work with databases using Python objects, abstracting away much of the SQL, making database interactions more intuitive and less error-prone.
-
Alembic: Alembic, designed to work with SQLAlchemy, manages database migrations. As your application grows and changes, so too will your database schema. Alembic helps manage these changes, ensuring data integrity.
Database Diagram: Tables and Relations¶
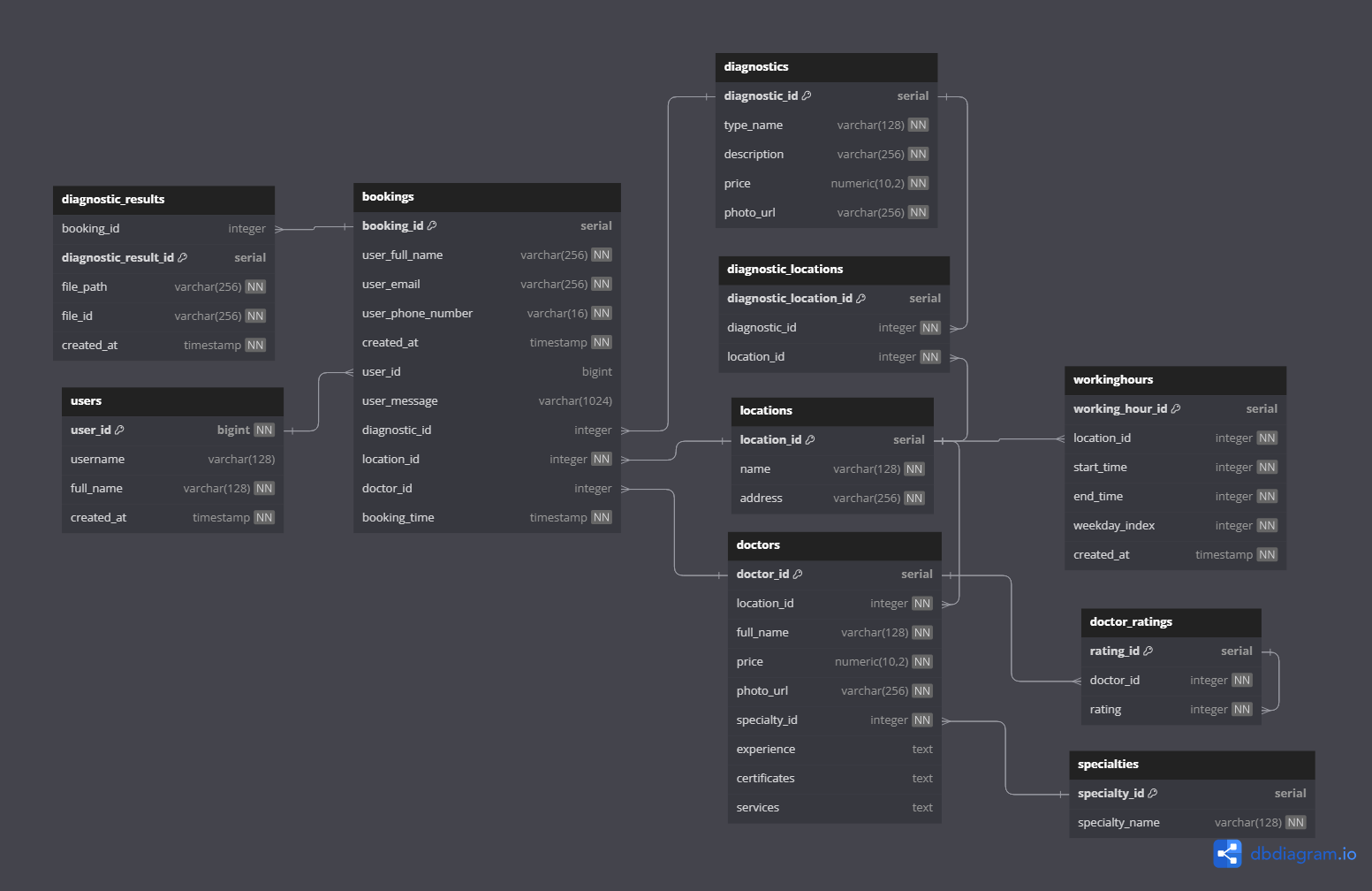
User, Bookings, and Diagnostic Results¶
erDiagram
bookings ||..|o diagnostic_results : produces
users ||..|o bookings : makes
users ||..|o diagnostic_results : receivesIn this design:
- A user can make multiple bookings (either with doctors or diagnostics).
- Each booking can produce multiple diagnostic results.
- A user can directly receive multiple diagnostic results.
Doctors, Ratings, and Locations¶
erDiagram
doctors ||..|o doctor_ratings : receives
doctors ||..|| specialties : belongs_to
doctors ||..|| locations : works_at
doctors ||..|o bookings : receivesKey points:
- Doctors receive ratings from users.
- Every doctor belongs to a specific specialty.
- Doctors work at particular locations.
- Doctors can receive multiple bookings.
Locations, Diagnostic Locations, and Working Hours¶
erDiagram
locations ||..|| diagnostic_locations : has
locations ||..|| workinghours : has
locations ||..|o bookings : atFrom the design:
- Locations (clinics) can have multiple diagnostic locations.
- Each location also has designated working hours.
- Bookings can be made at different locations.
Diagnostics and Their Locations¶
erDiagram
diagnostics ||..|| diagnostic_locations : has
diagnostics ||..|o bookings : involvesMain points:
- Specific diagnostics are available at certain locations, represented by diagnostic locations.
- Diagnostics can be involved in multiple bookings.
Deep Dive: Doctors Table¶
The Doctors table, as represented in the SQLAlchemy model:
Example
See full code in doctors.py
from typing import Optional
from sqlalchemy import Integer, String, ForeignKey, DECIMAL, TEXT
from sqlalchemy.orm import Mapped, mapped_column
from .base import Base, TableNameMixin, TimestampMixin, int_pk
class Doctor(Base, TableNameMixin):
doctor_id: Mapped[int_pk]
location_id: Mapped[int] = mapped_column(ForeignKey("locations.location_id"))
full_name: Mapped[str] = mapped_column(String(128))
specialty_id: Mapped[int] = mapped_column(ForeignKey("specialties.specialty_id"))
price: Mapped[float] = mapped_column(DECIMAL(10, 2))
photo_url: Mapped[str] = mapped_column(String(256))
experience: Mapped[Optional[str]] = mapped_column(TEXT)
certificates: Mapped[Optional[str]] = mapped_column(TEXT)
services: Mapped[Optional[str]] = mapped_column(TEXT)
-
Here, the
Doctorclass represents thedoctorstable in the database. -
Each attribute in the class corresponds to a column in the table. The type and constraints of these columns are defined using SQLAlchemy's API.
Working with the Data: Requests Repository¶
The DoctorRepo class showcases how the data stored in the doctors table can be accessed and manipulated using SQLAlchemy's ORM capabilities:
Example
See full code in doctors.py
from sqlalchemy import select
from infrastructure.database.models import (
Doctor,
Booking,
DoctorRating,
Location,
)
from infrastructure.database.models.doctors import Specialty
from infrastructure.database.repo.base import BaseRepo
class DoctorRepo(BaseRepo):
async def get_all_doctors(self) -> list[Doctor]:
stmt = (
select(
...
)
)
result = await self.session.execute(stmt)
return result.mappings().all()
async def get_specialties(self) -> list[Specialty]:
stmt = (
select(Specialty)
...
)
result = await self.session.execute(stmt)
return result.mappings().all()
-
DoctorRepocontains methods that fetch all doctors and their specialties. -
These methods utilize the
selectfunction from SQLAlchemy to create a SQL SELECT statement.
After that, we import and use the DoctorRepo as a property of the RequestsRepo class:
Example
See full code in requests.py
@dataclass
class RequestsRepo:
"""
Repository for handling database operations. This class holds all the repositories for the database models.
You can add more repositories as properties to this class, so they will be easily accessible.
"""
session: AsyncSession
@property
def users(self) -> UserRepo:
return UserRepo(self.session)
@property
def doctors(self) -> DoctorRepo:
return DoctorRepo(self.session)
# other repos...