Telegram WebApp Integration Features in MedSync¶
Overview
Understanding how MedSync seamlessly integrates with Telegram is pivotal for both developers and users.
By ensuring a cohesive experience, users can enjoy the capabilities of MedSync without ever feeling that they've departed from the familiar Telegram interface. This guide provides a detailed overview of the features and integrations MedSync leverages from Telegram.
1. Dynamic Theming with SCSS Variables¶
Info
Dynamic theming allows a web application to adjust its appearance according to user preferences or system settings, leading to improved user experience and interface consistency.
MedSync leverages this by integrating Telegram theme parameters to adjust the interface based on the Telegram user's current theme.
Understanding the Theme Parameters¶
The Telegram Mini Apps can fetch the user's theme settings. These settings, formatted in CSS custom properties (var(--property-name)), can be directly accessed and applied within our SCSS.
For instance, var(--tg-theme-bg-color) fetches the background color from the Telegram theme settings.
Utilizing SCSS¶
In our project we have a _vars.scss file, that centralizes all the color and style variables, providing easy access and modification capabilities.
To integrate the Telegram theme parameters, we've used the following syntax (you can still use var(--property-name), but we wanted to have all scss variables in a separate file):
$tg-theme-bg : var(--tg-theme-bg-color);
$tg-theme-secondary-bg: var(--tg-theme-secondary-bg-color);
$tg-theme-text: var(--tg-theme-text-color);
$tg-theme-hint: var(--tg-theme-hint-color);
$tg-theme-button: var(--tg-theme-button-color);
$tg-theme-button-text: var(--tg-theme-button-text-color);
$color-box-shadow: var(--tg-theme-secondary-bg-color);
How to Apply theme colors¶
| Element | Variable | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Main Background | --tg-theme-bg-color |
The primary background color of the application. |
| Elements Background | --tg-theme-secondary-bg-color |
Use for components like cards or modals to contrast with the main background. |
| Text | --tg-theme-text-color |
Standard text color for most website content. |
| Headers & Titles | --tg-theme-text-color |
Distinct color for main headings, using the primary text color for uniformity. |
| Subheaders | --tg-theme-hint-color |
A slightly subdued color, ideal for subheadings or secondary titles. |
| Borders & Dividers | --tg-theme-secondary-bg-color |
Suitable for differentiating sections or separating items in a list. |
| Hints & Inactive Text & Placeholders & Icons | --tg-theme-hint-color |
Perfect for secondary information, tooltips, or less prominent icons. |
| Buttons (Background) | --tg-theme-button-color |
A contrasting color to ensure buttons stand out and are easily clickable. |
| Buttons (Text) | --tg-theme-button-text-color |
Provides an optimal contrast against the button's background color. |
| Links | --tg-theme-link-color |
Clearly distinguishes hyperlinks from standard text. |
Use this link to read more about Telegram theme parameters.
Practical Application
The .search-bar class showcases how these variables are applied in practice:
- The input field’s border and background colors use the
$tg-theme-secondary-bgvariable, effectively adapting to the Telegram theme. - The text color for the input adapt based on the
$tg-theme-textvariable. - The placeholder text color is set to
$tg-theme-hintto provide a subtle contrast with the input text.
.search-bar {
&__input {
border: 1px solid $tg-theme-secondary-bg;
background: $tg-theme-secondary-bg;
color: $tg-theme-text;
//... other styles
input::placeholder {
color: $tg-theme-hint;
}
}
// ... other styles
&__icon {
&__img {
stroke: $tg-theme-text;
}
}
}
2. Haptic Feedback¶
Info
Haptic feedback is the use of touch sensations, like vibrations, to convey information or specific events within an application. It's an essential aspect of user experience, adding depth and tactile responses to user actions.
Integration¶
Telegram provides developers with a set of haptic feedback methods to enrich user interactions. These methods can produce different touch sensations based on the specific events in the application.
Refer to Telegram's documentation for more details on the available methods.
impactOccurred(style): Triggers when a collision or impact event happens within the UI. The style parameter dictates the strength and type of haptic feedback.notificationOccurred(type): Indicates the completion, failure, or warning of an action. The type parameter specifies the kind of feedback.selectionChanged(): Activates when the user alters a selection. It is used to denote a change but not the actual selection or confirmation of an item.
Haptic Feedback in MedSync¶
Using in React¶
In our React app we used a special hook from the library "@vkruglikov/react-telegram-web-app
import {useHapticFeedback} from "@vkruglikov/react-telegram-web-app";
// ...
const [impactOccurred, notificationOccurred, selectionChanged] = useHapticFeedback();
// just call the function when you need it
selectionChanged()
Examples¶
Here's how we've strategically employed haptic feedback within MedSync:
-
Initial Selection: When a user first chooses an option, like picking a doctor or medical specialty, we use
notificationOccurred("success"). This provides a gentle confirmation to the user, assuring them of their successful selection. -
Modification of Selection: In cases where users already have a selection and decide to change or remove it, the method
selectionChanged()is triggered. This delivers a subtle sensation indicating that a prior choice has been altered. -
Primary Action Confirmation: Upon pressing the main action button,
notificationOccurredis invoked, offering a tactile affirmation of the action.
The sensations resulting from these methods
selectionChanged(): Provides a soft, subtle pulse, indicating a change or shift.notificationOccurred("success"): This feels more pronounced, marking the importance or culmination of a series of actions.
3. CloudStorage¶
Info
Telegram's CloudStorage feature acts as an agile solution to manage user data securely and efficiently, directly from the Telegram interface.
MedSync employs this feature to store and retrieve essential user information, such as selected doctors, diagnostic details, and clinic locations.
Telegram's CloudStorage Features¶
Telegram's CloudStorage provides a set of methods for developers to store and access data:
setItem: Allows the storage of a value against a specific key.getItem: Retrieves a value using the provided key.getItems: Fetches multiple values using an array of keys.removeItem: Deletes a specific value using its key.removeItems: Removes multiple values using their respective keys.getKeys: Obtains a list of all keys stored in the cloud storage.
Each of these methods offers developers flexibility in how they manage and interact with user data.
Implementation in MedSync¶
A Finite State Machine (FSM) is a computational model that operates based on a current state.
It can change from one state to another in response to external inputs. We use cloudStorage essentially as a storage for our FSM.
Tip
You can use it also for storing the actual states of your users! Therefore, they can continue from where they left off, even if they close the web app.
Using in React¶
In our React app we used a special hook from the library "@vkruglikov/react-telegram-web-app
import {useCloudStorage} from "@vkruglikov/react-telegram-web-app";
// ...
const storage = useCloudStorage()
// ...
await storage.setItem("selectedTimeSlot", JSON.stringify(selectedTimeSlot))
Examples¶
For instance, when a user selects a specific time slot for an appointment, it's stored using:
Similarly, when users provide data in an input form, it's saved like so:
Tip
This is particularly useful when users are required to fill out a form with multiple fields.
Once we save this, we can pre-fill the form with the saved data when the user returns to the page next time, or even if they close the web app and open it again.
To retrieve this information, we use:
Note the use of JSON.stringify and JSON.parse methods, which convert JavaScript objects to strings and vice versa. This ensures the correct format for storage and subsequent retrieval.
Note, that you're not restricted by the JSON format, it's just a convenient way to store data in a string format.
Storage Limitations
Keep in mind that there are constraints to using Telegram's CloudStorage. A bot can store up to 1024 items per user, with each key containing 1-128 characters, and values being 0-4096 characters long.
Now, when the user has finished with the form, we can remove the data from the storage:
4. Navigation with Telegram's Buttons¶
Info
Telegram provides specialized objects, BackButton and MainButton, to ensure user navigation within the Mini App environment is intuitive and seamless.
Understanding Button Objects¶
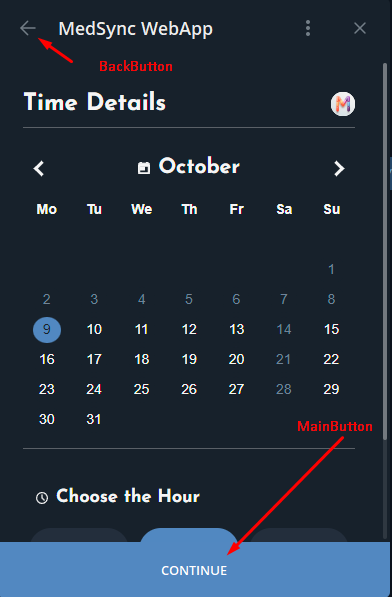
Telegram's Button features are designed to integrate natively into the Telegram Mini App interface:
- BackButton: Controls the back button displayed in the header, enabling users to return to previous pages.
- MainButton: Controls the primary action button, displayed at the bottom. It's used to confirm actions or proceed to the next step.
Each of these button objects offers methods to customize their appearance, set event handlers, and manage their visibility and activity state.
BackButton in MedSync¶
Using in React¶
import {BackButton} from "@vkruglikov/react-telegram-web-app";
// ...
const SlotSelection = ({storageKey, itemType}) => {
const navigate = useNavigate();
...
return ( <>
<BackButton onClick={() => navigate(-1)}/>
...
</>)
}
Warning
There are scenarios where back navigation might be restricted to prevent users from reverting essential or irreversible actions.
For instance, after a successful booking, we may opt to hide the BackButton to prevent users from navigating back and altering confirmed details.
MainButton in MedSync¶
Using in React¶
import {MainButton} from "@vkruglikov/react-telegram-web-app";
// ...
const SlotSelection = ({storageKey, itemType}) => {
const navigate = useNavigate()
// ...
const handleNext = async () => {
notificationOccurred("success");
// ...
navigate(`/booking/patient-info-form/${itemType}`);
};
return (<>
...
{selectedTimeSlot && (
<MainButton onClick={handleNext}></MainButton>
)}
</>)
}
In the above example, the MainButton is only displayed when a time slot is selected, ensuring users can't proceed without making a selection.
The button press triggers the handleNext function, which confirms the user's choice and navigates them to the next step.
5. Other WebApp Methods¶
Info
While external libraries offer a comfortable integration with the Telegram WebApp environment, there's no shame in directly tapping the Telegram's native WebApp methods.
These methods grant developers robust control over the Mini App's behavior, user interactions, and appearance.
Direct Usage¶
Telegram's WebApp methods give developers direct control over the app's appearance, behavior, and interaction within the Telegram interface: from controlling the app's header and background color, managing its expanded state, to showing pop-ups and reading clipboard contents.
Forced Expanded View¶
One of the very first things MedSync ensures upon opening is the full utilization of the available screen space. We achieve this by forcing the Mini App into its expanded view.
const App = () => {
useEffect(() => {
if (window.Telegram && window.Telegram.WebApp) {
window.Telegram.WebApp.expand();
}
}, []);
}
Enhanced Closing Control¶
To prevent users from unintentionally exiting the Mini App, especially when they're midway through making selections or providing essential information, MedSync activates the closing confirmation.
This ensures that even if users make the slide-down gesture (typically used to close apps), they are prompted for confirmation.
Forced App Closure¶
There might be instances when it's necessary to programmatically close the Mini App. This might be after a particular action has been confirmed, or some critical error has occurred.
You can programmatically trigger the app to close using:
Additional Integration Possibilities¶
While MedSync has used specific WebApp methods as per its requirements, the Telegram WebApp provides a plethora of other functionalities. Developers can show alerts, confirmations, scan QR codes, request user contacts, and so much more.
Tip
It's always a good practice to first check the availability of the window.Telegram.WebApp object before making any calls to ensure compatibility and avoid potential errors.
6. Securing User Data: Validating InitData¶
Understanding InitData¶
In Telegram's WebApp environment, InitData is a secure way of receiving initial data about the user.
This data can include the user's ID, their first and last name, and more.
Most importantly, InitData contains a hashed string that can be validated against the information provided, ensuring its genuineness.
Integrating in MedSync¶
Fetching InitData in React¶
To ensure we're working with the correct InitData, we utilize the useInitData hook:
import {useInitData} from "@vkruglikov/react-telegram-web-app";
const [InitDataUnsafe, InitData] = useInitData();
When sending data to our backend, we include this InitData:
const response = await axios.post(`${import.meta.env.VITE_REACT_APP_API_URL}/api/${itemType}/book_slot`, {
// ... other data ...
userInitData: InitData,
});
Backend Validation:¶
Once received in our backend, we validate the InitData using our bot's token.
@diagnostics_router.post("/book_slot")
async def book_slot(request: Request, repo: RequestsRepo = Depends(get_repo)):
data = await request.json()
init_data = data.get("initData")
if init_data and not validate_telegram_data(init_data):
raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail="Invalid initData")
# ... rest of the method ...
The heart of the validation process is the validate_telegram_data function:
Example
See full code in utils.py
def validate_telegram_data(init_data: str) -> bool:
# ... parsing and constructing data-check-string ...
# Computing the secret key
secret_key = hmac.new(b"WebAppData", config.tg_bot.token.encode(), hashlib.sha256).digest()
# Comparing received hash with computed hash
computed_hash = hmac.new(secret_key, data_check_string.encode(), hashlib.sha256).hexdigest()
# ... additional checks ...
return True
This method:
- Parses the received data.
- Constructs a verification string (
data-check-string). - Computes a hash of this string using our bot token.
- Compares the received hash with the computed hash.
- Checks if the data is outdated.
Security First!
Always ensure that any data you receive from client-side applications is validated in the backend. Trusting client-side data without validation can lead to severe security vulnerabilities, like exposing bot token.